The Mediterranean Diet, according to medical and wellness studies, is the best nutritional regime one could possibly follow. Such a diet follows the eating habits of mainly the Italian, Greek and Spanish cultures that tend to consume foods rich in fibres, loads of fresh fruits and vegetables, and prefer using olive oil rather than butter or margarine to season and cook.
Then basic products that make up this extremely healthy and refreshing diet can be divided into 6 main groups:
1) Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
These should be consumed on a daily basis, especially for breakfast or as a snack during the afternoon. It would be preferable to follow the seasonality of the produce, in order to be sure it is fresh and free from pesticides, and to eat it uncooked to ensure the right intake of vitamins.
2) Unrefined Whole Grain Cereal
These include: brown rice, multigrain bread, oats, whole wheat and whole grain flour. The main characteristic of these products is that they have a complex structure, which means that they aren’t absorbed as fast as simple carbs, leaving you feeling full longer.
3) Legumes
These are basically seeds coming from plants and include: beans, peas, chickpeas, soybeans, lentils and nuts. Legumes are rich in iron and are a consistent source of protein. They can be a great substitute for red meat providing the same amount of protein but virtually no saturated fats.
4) Lean Meats
These types of meats are very low in fats. They can include: turkey, chicken, lamb, game and some particularly lean cuts of beef. It is always preferable to limit the weekly amount of meat intake to 1 to 2 servings.
5) Fish
Fish is a great source of Omega3 fatty acids, which have an anti-inflammatory and heart protective action and also contains iron and phosphorus, which are fundamental for nerve and muscle health. Fish is a great alternative to red meat and should be consumed 2 to 3 times per week.
6) Olive Oil
Olive oil is the best fat available for human consumption. It is a far better choice compared to butter, margarine or any other highly saturated fat. Pressing whole olives reducing them to a viscous liquid produces olive oil. The best pressing technique does not involve any heating (cold pressed), keeping this way all the vitamins and nutrients of the olives in the product. Olive oil is the heart of the Mediterranean Diet.
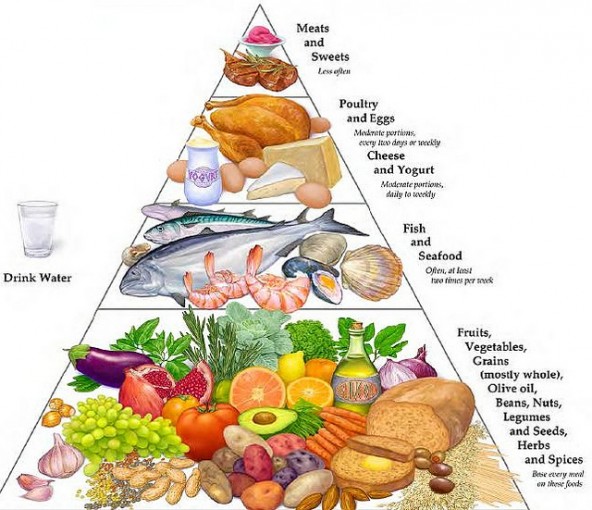
Now that the food groups are clearly categorized, it is important to understand the quantity of their daily intake and the right combinations in order to follow the Mediterranean Diet correctly. The easiest way to organize a food plan is to keep in mind the food pyramid, eliminating the saturated fats almost completely and keeping red meat and sugar consumption to minimum.
If you observe the above pyramid you will notice that the base of the diet consists of fresh fruits and vegetables. The servings of this category of food are between 6 and 12 servings per day. Next you get the unrefined cereal servings, which should be around 4 to 6 per day. Two to three spoons of olive oil complete the basics of the Mediterranean Diet. Fish, poultry and dairy products should be added in small amounts, preferring fish to the rest. Avoiding sugars, red meats and saturated fats almost completely is the last step towards a healthy well-balanced diet.
The Mediterranean Diet is very easy to follow without a specific plan and will give great results also if you are aiming to loose weight. Remember to eat your fruits and vegetables uncooked and to use olive oil to season your dishes. Try to avoid refined grains, refined sugars, butter and any processed food.
These easy steps to a complete Mediterranean Diet will help you keep a healthy and fit lifestyle.
For inspiration be sure to take a look back at our recipe archives, they are full of simple but tasty Mediterranean dishes! And please send us your own favourite recipes so that we can share them!